Rem Turns the echo on so that each command will be shown as executed echo on echo 'Hello World' Rem Turns the echo off so that each command will not be shown when executed @echo off echo 'Hello World' Rem Displays the contents of the PATH variable echo%PATH% Output. The following output will be displayed in the command prompt. Windows 10 Activation Batch File. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets. Echo is a feature of batch files which repeats (echos) each line of the batch file to the screen as it is executed. Although useful for debugging purposes, once production is completed ECHO serves no purpose other than creating a messy screen which may confuse unsophisticated users. This is the beauty of batch files. The echo is used to display a message that is several lines long you can include several echo commands one after the other in your batch program. This is similar to printf function in C, we need not use any quotes to specify the message here. Content that immediately follows the echo command is printed. Command to turn on echo: @echo on. We can turn on or turn off echo at any point in a batch file. For example, you may want echo to be on for certain commands in the batch file, and then you may turn it off, and then again you can turn it on.
Selects and runs a command on a file or set of files. This command is most commonly used in batch files.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
/P <pathname> | Specifies the path from which to start the search. By default, searching starts in the current working directory. |
/M <searchmask> | Searches files according to the specified search mask. The default searchmask is *. |
| /S | Instructs the forfiles command to search in subdirectories recursively. |
/C <command> | Runs the specified command on each file. Command strings should be wrapped in double quotes. The default command is 'cmd /c echo @file'. |
/D [{+|-}][{<date> | <days>}] | Selects files with a last modified date within the specified time frame:
|
| /? | Displays the help text in the cmd window. |
Remarks
The
forfiles /Scommand is similar todir /S.You can use the following variables in the command string as specified by the /C command-line option:
Variable Description @FILE File name. @FNAME File name without extension. @EXT File name extension. @PATH Full path of the file. @RELPATH Relative path of the file. @ISDIR Evaluates to TRUE if a file type is a directory. Otherwise, this variable evaluates to FALSE. @FSIZE File size, in bytes. @FDATE Last modified date stamp on the file. @FTIME Last modified time stamp on the file. The forfiles command lets you run a command on or pass arguments to multiple files. For example, you could run the type command on all files in a tree with the .txt file name extension. Or you could execute every batch file (*.bat) on drive C, with the file name Myinput.txt as the first argument.
This command can:
Select files by an absolute date or a relative date by using the /d parameter.
Build an archive tree of files by using variables such as @FSIZE and @FDATE.
Differentiate files from directories by using the @ISDIR variable.
Include special characters in the command line by using the hexadecimal code for the character, in 0xHH format (for example, 0x09 for a tab).
This command works by implementing the
recurse subdirectoriesflag on tools that are designed to process only a single file.
Examples
Batch File Echo Off
To list all of the batch files on drive C, type:
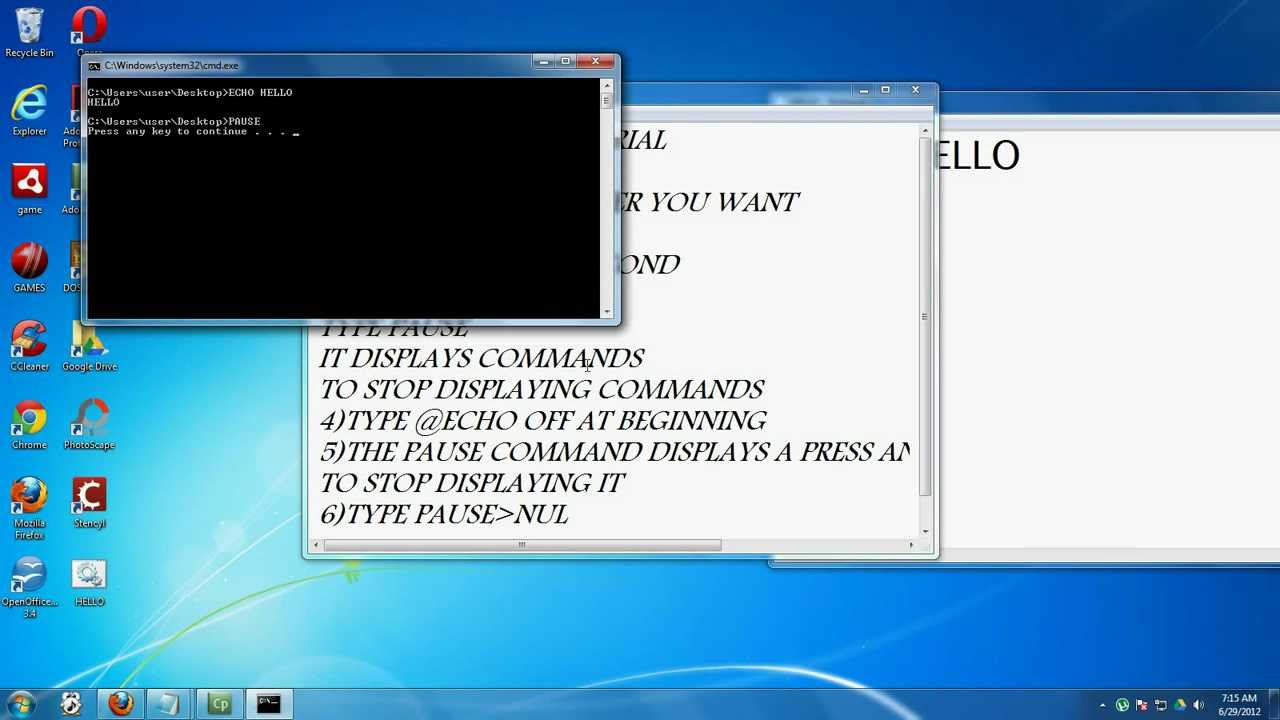
To list all of the directories on drive C, type:
Batch File Echo Variable
To list all of the files in the current directory that are at least one year old, type:
To display the text file is outdated for each of the files in the current directory that are older than January 1, 2007, type:
To list the file name extensions of all the files in the current directory in column format, and add a tab before the extension, type:
Echo Batch File
Additional References
